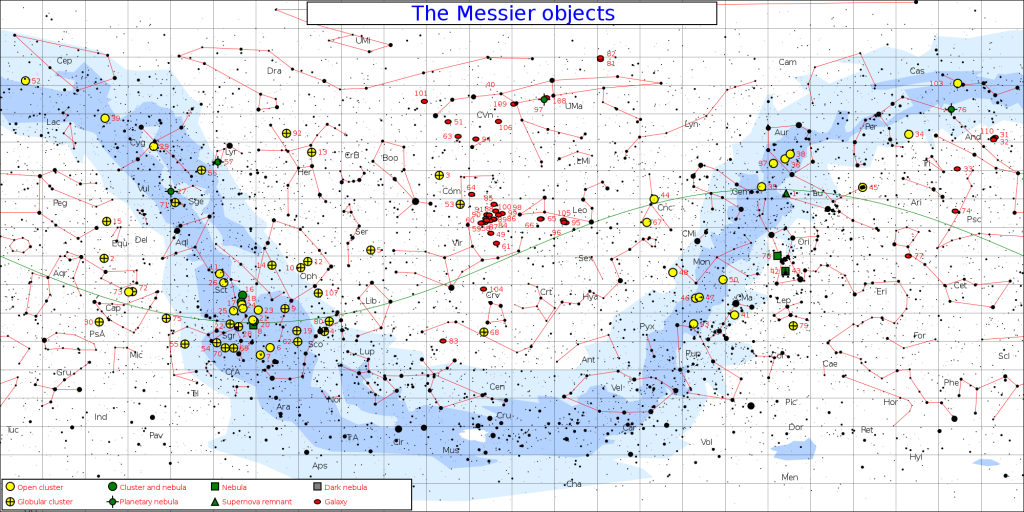
The Messier objects are a group of deep sky objects catalogued by the French astronomer Charles Messier in the late 18th century.
Messier’s Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d’Étoiles (Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters) is a collection of deep sky objects (galaxies, nebulae, star clusters) and other astronomical objects (asterisms, binary stars) that were visible with binoculars and telescopes at the time.
Messier compiled the list between 1758 and 1782. His original goal was to list the objects that were frequently confused for comets. He was a comet hunter, which was a popular activity among 18th century astronomers, and this led him to create the first comprehensive list of deep sky objects that frustrated his search.
The Italian astronomer Giovanni Hodierna had compiled a similar catalogue of astronomical objects, about 40 of them, and published it in 1654, but his work had no major impact and Messier was likely unaware of it.
The Messier objects are popular targets among amateur astronomers because they are relatively bright and easy to find and observe in small telescopes. Messier himself used a relatively small refractor telescope (4 inch, or 100 mm) for his observations. In the early spring, all the objects can be seen over the course of a single night.

The Ptolemy Cluster (Messier 7), image: NASA
Messier made his observations from Paris, France, which is why his catalogue doesn’t include prominent deep sky objects that can only be seen from the southern hemisphere, such as the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
The southernmost object on Messier’s list is Messier 7, the Ptolemy Cluster, an open cluster in Scorpius constellation, found at declination -34°47’34’’. At magnitude 3.3, the cluster is bright enough to be seen from the northern hemisphere in the summer months.
Messier’s list includes almost all the best examples of different types of deep sky objects – galaxies, open clusters, globular clusters, planetary nebulae, and diffuse nebulae – that can be observed from Europe. Most Messier objects are among the nearest examples of their class to Earth and can be seen in great detail with larger instruments, which makes them popular targets for study among professional astronomers as well.
Messier’s catalogue was first published in “Mémoires de l’Academie“, the journal of the French Academy of Sciences in Paris in 1774, and the final version came out in 1781, in Connaissance des temps for 1784, an official astronomical annual publication in France.
The original catalogue included 45 deep sky objects, and the 1781 version had 103.
Today’s versions of Messier’s catalogue contain 110 objects, as they include objects that were observed by Messier and his colleague Pierre Méchain after the catalogue was published. The final seven Messier objects – M104 to M110 – were added by astronomers and historians between 1921 and 1966 after discovering evidence that the objects were observed either by Messier or Méchain.
Messier 104 was added by the French astronomer and author Nicolas Camille Flammarion in 1921, objects M105 to M107 were added by the Canadian astronomer Helen Sawyer Hogg in 1947, M108 and M109 were added by the American astronomer Owen Gingerich in 1960, and the last one, M110, was added by the Welsh astronomer Kenneth Glyn Jones in 1967.
MESSIER OBJECTS MAP
MESSIER OBJECTS LIST

This image of the Crab combines data from three of NASA’s Great Observatories. X-rays from Chandra (blue) have been combined with optical images from Hubble (red and yellow) as well as infrared data from Spitzer (purple). Together, these three telescopes provide a striking view of this famous cosmic source. Image: Joseph DePasquale, Chandra X-Ray Observatory
Messier 1 (M1)
Messier 1 (NGC 1952), also known as the Crab Nebula, is a supernova remnant in Taurus constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 9.0 and is approximately 6,300 light years distant.
Messier 2 (M2)
Messier 2 (NGC 7089) is a globular cluster in Aquarius constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 7.5 and is 36,000 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 3 (M3)
Messier 3 (NGC 5272) is a globular cluster located in Canes Venatici constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 7.0 and is approximately 31,000 light years distant.
Messier 4 (M4)
Messier 4 (NGC 6121) is a globular cluster in Scorpius. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 7.5 and is approximately 7,000 light years distant.
Messier 5 (M5)
Messier 5 (NGC 5904) is a globular cluster in Serpens constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 7.0 and is about 23,000 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 6 (M6)
Messier 6 (NGC 6405), also known as the Butterfly Cluster, is an open cluster in Scorpius constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.5 and is approximately 2,000 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 7 (M7)
Messier 7 (NGC 6475), also known as the Ptolemy Cluster, is an open cluster in Scorpius. It has a visual magnitude of 3.5 and is about 1,000 light years distant.

Lagoon Nebula (Messier 8), image: ESO/IDA/Danish 1.5 m/ R. Gendler, U.G. Jørgensen, K. Harpsøe
Messier 8 (M8)
Messier 8 (NGC 6523), better known as the Lagoon Nebula, is a nebula associated with a cluster located in Sagittarius. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.0 and is approximately 6,500 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 9 (M9)
Messier 9 (NGC 6333) is a globular cluster in Ophiuchus constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 9.0 and is about 26,000 light years distant.
Messier 10 (M10)
Messier 10 (NGC 6254) is a globular cluster in Ophiuchus. It has an apparent magnitude of 7.5 and is about 13,000 light years distant from the Sun.
Messier 11 (M11)
Messier 11 (NGC 6705), popularly known as the Wild Duck Cluster, is an open star cluster located in Scutum constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 7.0 and is approximately 6,000 light years distant.
Messier 12 (M12)
Messier 12 (NGC 6218) is a globular cluster in Ophiuchus. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.0 and is about 18,000 light years distant.
Messier 13 (M13)
Messier 13 (NGC 6205), also known as the Great Globular Cluster in Hercules, is as the name says, a globular cluster located in Hercules constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.8 and is approximately 22,000 light years distant.
Messier 14 (M14)
Messier 14 (NGC 6402) is a globular cluster in Ophiuchus constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 9.5 and is approximately 27,000 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 15 (M15)
Messier 15 (NGC 7078) is a globular cluster in Pegasus constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.2 and is about 33,000 light years distant.
Messier 16 (M16)
Messier 16 (NGC 6611), also known as the Eagle Nebula, is a nebula with a cluster located in Serpens constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.5 and is approximately 7,000 light years distant.

Omega Nebula (Messier 17), image: Adam Block/Mount Lemmon SkyCenter/University of Arizona (CC BY-SA 4.0)
Messier 17 (M17)
Messier 17 (NGC 6618), also known as the Omega Nebula (or Swan, Horseshoe, or Lobster Nebula), is a nebula with a cluster in Sagittarius constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 6.0 and is about 5,000 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 18 (M18)
Messier 18 (NGC 6613) is an open cluster in Sagittarius. It has a visual magnitude of 8.0 and is approximately 6,000 light years distant.
Messier 19 (M19)
Messier 19 (NGC 6273) is a globular cluster in Ophiuchus. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.5 and is approximately 27,000 light years distant.

The central region of the Trifid Nebula (M20). Image: Subaru Telescope (NAOJ), Hubble Space Telescope, Martin Pugh; Processing: Robert Gendler
Messier 20 (M20)
Messier 20 (NGC 6514), also known as the Trifid Nebula, is a nebula with a cluster located in Sagittarius constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.3 and is about 5,200 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 21 (M21)
Messier 21 (NGC 6531) is an open cluster in Sagittarius. It has a visual magnitude of 7.0 and is about 3,000 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 22 (M22)
Messier 22 (NGC 6656), also known as the Sagittarius Cluster, is a globular cluster in Sagittarius. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.1 and is approximately 10,000 light years distant.
Messier 23 (M23)
Messier 23 (NGC 6494) is an open cluster in Sagittarius constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 6.0 and is approximately 4,500 light years distant from the Sun.
Messier 24 (M24)
Messier 24 (IC 4715), also known as the Sagittarius Star Cloud, is a Milky Way star cloud with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.6, approximately 10,000 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 25 (M25)
Messier 25 (IC 4725) is an open cluster located in Sagittarius. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.9 and is about 2,000 light years distant.
Messier 26 (M26)
Messier 26 (NGC 6694) is an open cluster in Scutum constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 9.5 and is about 5,000 light years distant from the Sun.
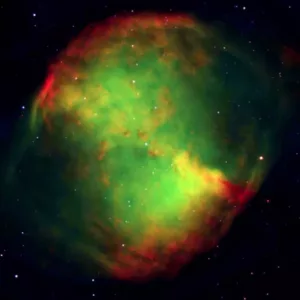
The Dumbbell Nebula, image: ESO
Messier 27 (M27)
Messier 27 (NGC 6853), also known as the Dumbbell Nebula, is a planetary nebula in Vulpecula constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 7.5 and is 1,250 light years distant.
Messier 28 (M28)
Messier 28 (NGC 6626) is a globular cluster is Sagittarius. It has a visual magnitude of 8.5 and is about 18,000 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 29 (M29)
Messier 29 (NGC 6913) is an open cluster located in the constellation Cygnus, the Swan. It has a visual magnitude of 9.0 and is about 7,200 light years distant.
Messier 30 (M30)
Messier 30 (NGC 7099) is a globular cluster in Capricornus constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.5 and is approximately 25,000 light years distant.

Andromeda Galaxy (Messier 31), image: Ivan Bok (CC BY 4.0)
Messier 31 (M31)
Messier 31 (NGC 224), better known as the Andromeda Galaxy, is a spiral galaxy in Andromeda constellation.
It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.4 and is approximately 2.5 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 32 (M32)
Messier 32 (NGC 221) is a dwarf elliptical galaxy located in Andromeda constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 8.1 and is approximately 2.9 million light years distant.
Messier 33 (M33)
Messier 33 (NGC 598), also known as the Triangulum Galaxy, is a spiral galaxy located in Triangulum constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.7 and is approximately 2.81 million light years distant from the Sun.
Messier 34 (M34)
Messier 34 (NGC 1039) is an open cluster located in Perseus constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.0 and is approximately 1,400 light years distant.
Messier 35 (M35)
Messier 35 (NGC 2168) is an open cluster in Gemini constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.5 and is about 2,800 light years distant from the Sun.
Messier 36 (M36)
Messier 36 (NGC 1960) is an open cluster in the constellation Auriga, the Charioteer. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.5 and is approximately 4,100 light years distant.
Messier 37 (M37)
Messier 37 (NGC 2099) is an open cluster in Auriga constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 6.0 and is about 4,600 light years distant.
Messier 38 (M38)
Messier 38 (NGC 1912) is an open star cluster in Auriga. It has an apparent magnitude of 7.0 and is about 4,200 light years distant.
Messier 39 (M39)
Messier 39 (NGC 7092) is an open cluster in Cygnus constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.5 and is about 800 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 40 (M40)
Messier 40 (Winnecke 4) is a double star, some 500 light years distant from Earth, located in the direction of Ursa Major constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 9.0.
Messier 41 (M41)
Messier 41 (NGC 2287) is an open cluster in Canis Major. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.5 and is about 2,300 light years distant.

Orion Nebula, image: Ljubinko Jovanovic
Messier 42 (M42)
Messier 42 (NGC 1976), the famous Orion Nebula, is a nebula located in the constellation Orion, the Hunter.
It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.0 and is approximately 1,600 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 43 (M43)
Messier 43 (NGC 1982), also known as De Mairan’s Nebula, is an H II region which is part of the Orion Nebula in Orion constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 7.0 and is about 1,600 light years distant from the Sun.
Messier 44 (M44)
Messier 44 (NGC 2632), also known as Praesepe or the Beehive Cluster, is an open cluster located in Cancer constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 3.7 and is approximately 600 light years distant.

The Pleiades, image: NASA, ESA, AURA, Caltech, Palomar Observatory
Messier 45 (M45)
Messier 45, better known as the Pleiades or Seven Sisters, is an open star cluster located in Taurus constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 1.6 and is about 400 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 46 (M46)
Messier 46 (NGC 2437) is an open cluster with an apparent magnitude of 6.5. It lies about 5,400 light years from Earth in the direction of Puppis constellation.
Messier 47 (M47)
Messier 47 (NGC 2422) is an open cluster in Puppis. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.5 and is about 1,600 light years distant.
Messier 48 (M48)
Messier 48 (NGC 2548) is an open cluster in the constellation Hydra, the Water Snake. It has a visual magnitude of 5.5 and is approximately 1,500 light years distant.
Messier 49 (M49)
Messier 49 (NGC 4472) is an elliptical galaxy located in Virgo constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 10.0 and is approximately 60 million light years distant from the solar system.
Messier 50 (M50)
Messier 50 (NGC 2323) is an open star cluster in the constellation Monoceros, the Unicorn. It has a visual magnitude of 7.0 and is approximately 3,000 light years distant from Earth.

Whirpool Galaxy (Messier 51), image: NASA, ESA, S. Beckwith (STScI), and The Hubble Heritage Team STScI, AURA)
Messier 51 (M51)
Messier 51 (NGC 5194, NGC 5195), the famous Whirlpool Galaxy, is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Canes Venatici, the Hunting Dogs. The galaxy has a visual magnitude of 8.4 and is approximately 37 million light years distant.
Messier 52 (M52)
Messier 52 (NGC 7654) is an open cluster in Cassiopeia constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.0 and is about 7,000 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 53 (M53)
Messier 53 (NGC 5024) is a globular star cluster in the constellation Coma Berenices, Berenice’s Hair. The cluster has a visual magnitude of 8.5 and is approximately 56,000 light years distant.
Messier 54 (M54)
Messier 54 (NGC 6715) is a globular cluster with an apparent magnitude of 8.5. It is located in Sagittarius constellation, about 83,000 light years from Earth.
Messier 55 (M55)
Messier 55 (NGC 6809) is a globular star cluster in Sagittarius. It has a visual magnitude of 7.0 and is approximately 17,000 light years distant.
Messier 56 (M56)
Messier 56 (NGC 6779) is a globular cluster in Lyra constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 9.5 and is approximately 32,000 light years distant.
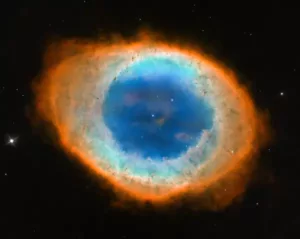
The Ring Nebula (M57), image: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage (STScI / AURA) – ESA / Hubble Collaboration
Messier 57 (M57)
Messier 57 (NGC 6720), better known as the Ring Nebula, is a planetary nebula located in Lyra. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 8.8 and is approximately 2,300 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 58 (M58)
Messier 58 (NGC 4579) is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It has a visual magnitude of 11.0 and is approximately 60 million light years distant.
Messier 59 (M59)
Messier 59 (NGC 4621) is an elliptical galaxy in Virgo. It has an apparent magnitude of 11.5 and is approximately 60 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 60 (M60)
Messier 60 (NGC 4649) is an elliptical galaxy in Virgo constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 10.5 and is approximately 60 million light years distant.
Messier 61 (M61)
Messier 61 (NGC 4303) is a spiral galaxy in Virgo. It has an apparent magnitude of 10.5 and is about 60 million light years distant.
Messier 62 (M62)
Messier 62 (NGC 6266) is a globular cluster located in the constellation Ophiuchus, the Serpent Bearer. It has a visual magnitude of 8.0 and is about 22,000 light years distant from Earth.
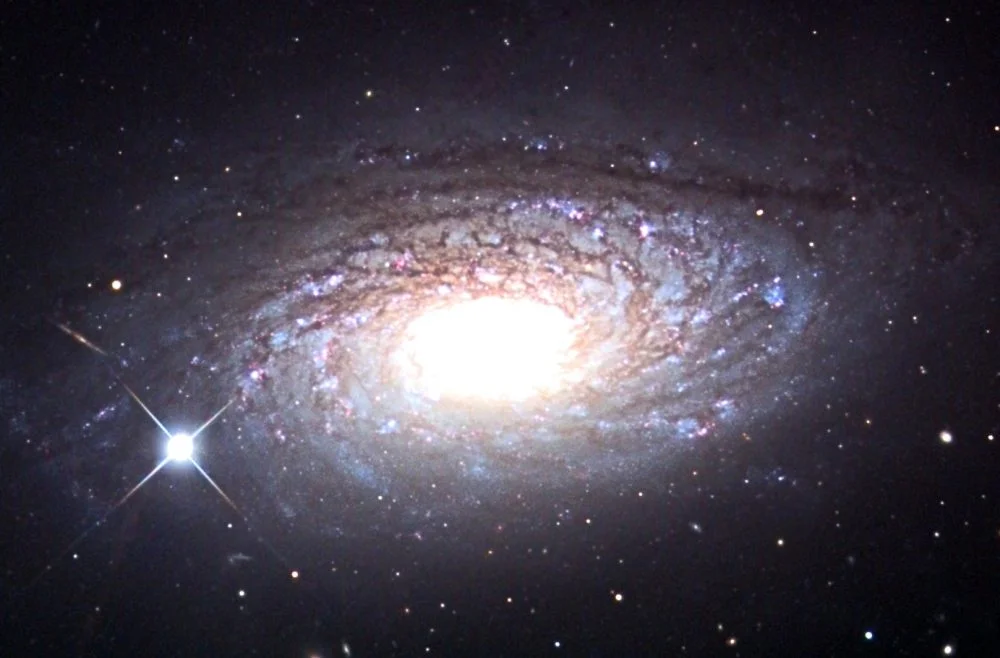

Sunflower Galaxy (Messier 63), image: Wikimedia Commons/Jschulman555
Messier 63 (M63)
Messier 63 (NGC 5055), also known as the Sunflower Galaxy, is a spiral galaxy in Canes Venatici constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.5 and is about 37 million light years distant.
Messier 64 (M64)
Messier 64 (NGC 4826), better known as the Black Eye Galaxy, is a spiral galaxy in Coma Berenices constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 9.0 and is approximately 12 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 65 (M65)
Messier 65 (NGC 3623) is a barred spiral galaxy that belongs to the Leo Triplet in Leo constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 10.5 and is about 35 million light years distant.
Messier 66 (M66)
Messier 66 (NGC 3627) is another barred spiral galaxy that belongs to the Leo Triplet of galaxies. It has an apparent magnitude of 10.0 and is located 35 million light years away in Leo constellation.
Messier 67 (M67)
Messier 67 (NGC 2682) is an open cluster in Cancer constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 7.5 and is about 2,250 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 68 (M68)
Messier 68 (NGC 4590) is a globular cluster in Hydra constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 9.0 and is approximately 32,000 light years distant from the Sun.
Messier 69 (M69)
Messier 69 (NGC 6637) is a globular star cluster in Sagittarius. It has a visual magnitude of 9.0 and is 25,000 light years distant.
Messier 70 (M70)
Messier 70 (NGC 6681) is a globular cluster in Sagittarius constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 9.0 and is about 28,000 light years distant.
Messier 71 (M71)
Messier 71 (NGC 6838) is a globular cluster in the constellation Sagitta, the Arrow. It has a visual magnitude of 8.5 and is approximately 12,000 light years distant.
Messier 72 (M72)
Messier 72 (NGC 6981) is a globular cluster in Aquarius. It has an apparent magnitude of 10.0 and is about 53,000 light years distant.
Messier 73 (M73)
Messier 73 (NGC 6994) is an asterism in Aquarius constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 9.0.

The grand-design spiral galaxy Messier 74 as photographed by the Hubble Space Telescope. Image: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage (STScI/AURA)-ESA, Hubble Collaboration. Acknowledgment: R. Chandar (University of Toledo) and J. Miller (University of Michigan)
Messier 74 (M74)
Messier 74 (NGC 628) is a spiral galaxy in Pisces constellation.
It has an apparent visual magnitude of 10.5 and is approximately 35 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 75 (M75)
Messier 75 (NGC 6864) is a globular cluster located in Sagittarius.
It has a visual magnitude of 9.5 and is about 58,000 light years distant.
Messier 76 (M76)
Messier 76 (NGC 650, NGC 651), also known as the Little Dumbbell Nebula, is located about 3,400 light years away in Perseus constellation. It is a planetary nebula with an apparent magnitude of 10.1.
Messier 77 (M77)
Messier 77 (NGC 1068), also known as Cetus A, is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Cetus, the Whale. It has a visual magnitude of 10.5 and is approximately 60 million light years distant.
Messier 78 (M78)
Messier 78 (NGC 2068) is a diffuse nebula in Orion constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 8.0 and is approximately 1,600 light years distant.
Messier 79 (M79)
Messier 79 (NGC 1904) is a globular cluster in the constellation Lepus, the Hare. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.5 and is 40,000 light years distant from the solar system.
Messier 80 (M80)
Messier 80 (NGC 6093) is a globular cluster in Scorpius. It has a visual magnitude of 8.5 and is about 27,000 light years distant.
Messier 81 (M81)
Messier 81 (NGC 3031), also known as Bode’s Galaxy, is a spiral galaxy in Ursa Major. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.9 and is approximately 12 million light years distant from the Sun.

Bode’s Galaxy and the Cigar Galaxy (M81 and M82), image: José Jiménez (CC BY 2.0)
Messier 82 (M82)
Messier 82 (NGC 3034), the famous Cigar Galaxy, is a starburst galaxy located in Ursa Major constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 9.5 and is 11 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 83 (M83)
Messier 83 (NGC 5236), better known as the Southern Pinwheel Galaxy, is a barred spiral galaxy in Hydra constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 8.5 and is approximately 10 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 84 (M84)
Messier 84 (NGC 4374) is a lenticular galaxy in Virgo. It has a visual magnitude of 11.0 and is approximately 60 million light years distant.
Messier 85 (M85)
Messier 85 (NGC 4382) is a lenticular galaxy in Coma Berenices constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 10.5 and is about 60 million light years distant from the Sun.
Messier 86 (M86)
Messier 86 (NGC 4406) is a lenticular galaxy located in Virgo. It has an apparent magnitude of 11.0 and is 60 million light years distant.
Messier 87 (M87)
Messier 87 (NGC 4486), also known as Virgo A, is an elliptical galaxy located in Virgo constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 11.0 and is 60 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 88 (M88)
Messier 88 (NGC 4501) is a spiral galaxy in Coma Berenices. It has an apparent magnitude of 11.0 and is approximately 60 million light years distant.
Messier 89 (M89)
Messier 89 (NGC 4552) is an elliptical galaxy in Virgo. It has a visual magnitude of 11.5 and is about 60 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 90 (M90)
Messier 90 (NGC 4569) is a spiral galaxy in Virgo constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 11.0 and is approximately 60 million light years distant.
Messier 91 (M91)
Messier 91 (NGC 4548) is a barred spiral galaxy located in Coma Berenices. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 11.0 and is approximately 60 million light years distant.
Messier 92 (M92)
Messier 92 (NGC 6341) is a globular star cluster in Hercules constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 7.5 and is about 26,000 light years distant.
Messier 93 (M93)
Messier 93 (NGC 2447) is an open cluster in Puppis constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 6.5 and is approximately 4,500 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 94 (M94)
Messier 94 (NGC 4736), also known as the Cat’s Eye Galaxy or Croc’s Eye Galaxy, is a spiral galaxy in Canes Venatici. It has a visual magnitude of 9.5 and is about 14.5 million light years distant.
Messier 95 (M95)
Messier 95 (NGC 3351) is a barred spiral galaxy in Leo constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 11.0 and is approximately 38 million light years distant.
Messier 96 (M96)
Messier 96 (NGC 3368) is a spiral galaxy in Leo. It has a visual magnitude of 10.5 and is about 38 million light years distant from Earth.
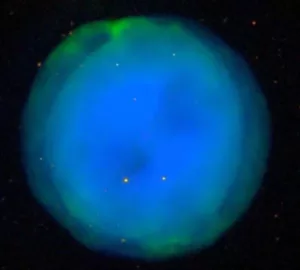
The Owl Nebula (Messier 97), image: Sloan Digital Sky Survey
Messier 97 (M97)
Messier 97 (NGC 3587), also known as the Owl Nebula, is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Ursa Major. It has a visual magnitude of 9.9 and is approximately 2,600 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 98 (M98)
Messier 98 (NGC 4192) is a spiral galaxy in Coma Berenices. It has a visual magnitude of 11.0 and is about 60 million light years distant.
Messier 99 (M99)
Messier 99 (NGC 4254) is a spiral galaxy in Coma Berenices. It has an apparent magnitude of 10.5 and is about 60 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 100 (M100)
Messier 100 (NGC 4321) is a spiral galaxy in Coma Berenices constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 10.5 and is approximately 60 million light years distant.
Messier 101 (M101)
Messier 101 (NGC 5457), the famous Pinwheel Galaxy, is a spiral galaxy in Ursa Major. It has a visual magnitude of 7.9 and is about 27 million light years distant.
Messier 102 (M102)
Messier 102 is listed as a galaxy, but the object has yet to be conclusively identified. The most likely candidate is the Spindle Galaxy (NGC 5866) in the constellation Draco.
Messier 103 (M103)
Messier 103 (NGC 581) is an open cluster in Cassiopeia constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 7.0 and is approximately 8,000 light years distant from Earth.

The Sombrero Galaxy (M104), image: NASA/ESA and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
Messier 104 (M104)
Messier 104 (NGC 4594), also known as the Sombrero Galaxy, is a spiral galaxy located in Virgo constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 9.5 and is approximately 50 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 105 (M105)
Messier 105 (NGC 3379) is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Leo. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 11.0 and is about 38 million light years distant from the Sun.
Messier 106 (M106)
Messier 106 (NGC 4258) is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. It has a visual magnitude of 9.5 and is about 25 million light years distant from the solar system.
Messier 107 (M107)
Messier 107 (NGC 6171) is a globular cluster in Ophiuchus constellation. It has a visual magnitude of 10.0 and is approximately 20,000 light years distant from Earth.
Messier 108 (M108)
Messier 108 (NGC 3556) is a barred spiral galaxy in Ursa Major constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 11.0 and is approximately 45 million light years distant from Earth.
Messier 109 (M109)
Messier 109 (NGC 3992) is a barred spiral galaxy located in Ursa Major. It has a visual magnitude of 11.0 and is about 55 million light years distant.
Messier 110 (M110)
Messier 110 (NGC 205) is a dwarf elliptical galaxy in Andromeda constellation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 10.0 and is approximately 2.2 million light years distant from Earth.