Caroline’s Rose Cluster is a bright open cluster located approximately 7,622 light-years away in the northern constellation Cassiopeia. With an apparent magnitude of 6.7, it is visible in binoculars and small telescopes. The cluster has the designation NGC 7789 in the New General Catalogue. It is one of the oldest open clusters known.
NGC 7789 is also known as the White Rose Cluster, Caroline’s Cluster, Caroline’s Rose, and Herschel’s Spiral Cluster. Visually, the looping pattern of stars and dark lanes in the cluster resembles that of rose petals.
The cluster has an estimated age of 1.7 billion years and is one of the older open clusters in the northern celestial hemisphere. In comparison, the Pleiades are 75 – 150 million years old and the Hyades have an estimated age of 625 million years.
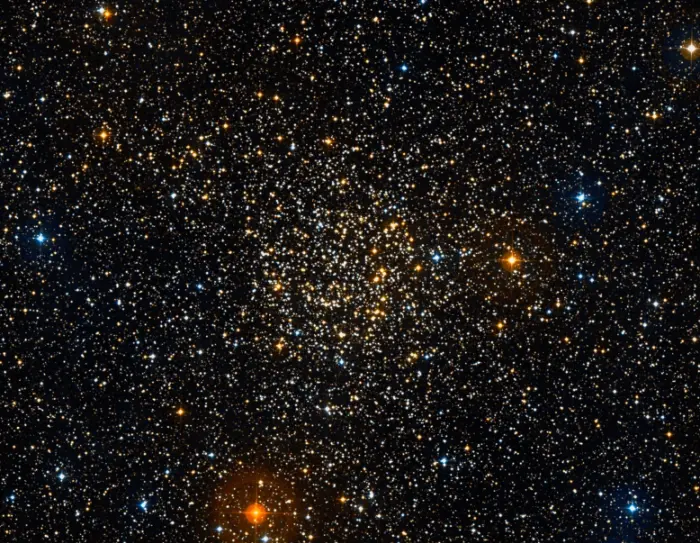

Caroline’s Rose Cluster (NGC 7789), image: Wikisky (DSS)
Caroline’s Rose has an apparent size of 16 arcminutes and a mass of 6,620.4 Suns. It contains about 1,000 members that shine at magnitude 11 to 18. It may have a total of up to 3,000 members. A 2021 study identified 2,799 cluster members within a radius of 28 arcminutes.
The brightest stars in the cluster are orange giants. Most other bright members are also evolved stars – giants and subgiants. More than a dozen blue stragglers have been identified in the cluster. These are stars that appear younger and bluer than expected for their evolutionary stage. They are hotter than main sequence stars in the cluster that are about to evolve into red giants. Blue stragglers are believed to be the result of stars colliding and producing higher-mass stars with higher temperatures.
Facts
NGC 7789 is named after the German-born British astronomer Caroline Herschel, who discovered it on November 1, 1783. Caroline’s brother William Herschel catalogued the cluster as H VI.30 on October 18, 1786. He described it as a “beautiful cluster of very compressed stars.”
Caroline’s Rose Cluster is one of the brightest and largest open star clusters in Cassiopeia, along with the Owl Cluster (NGC 457), Messier 52, Messier 103, NGC 654, and NGC 129. Caroline’s Cluster is slightly larger and fainter than the Owl Cluster, and both clusters are brighter and larger than the Messier clusters M52 and M103.
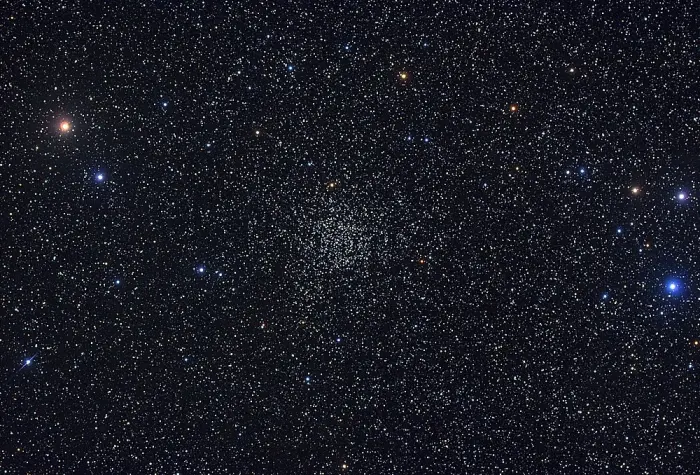

Caroline’s Rose Cluster (NGC 7789), image credit: Anton Vakulenko (CC BY-SA 2.0)
Location
Caroline’s Cluster lies in the region of Cassiopeia’s W, formed by the five brightest stars of Cassiopeia. The cluster can be found about 3 degrees southwest of Caph, the westernmost (or rightmost) star of the W asterism. It appears between the fifth magnitude stars Rho and Sigma Cassiopeiae. These stars are visible to the unaided eye right of Cassiopeia’s W on a clear night.
Caroline’s Rose Cluster can be seen in small binoculars. Small telescopes will reveal 40 – 50 members, while 8- and 10-inch telescopes will show up 100 – 150 stars within a diameter of 20 arcminutes.
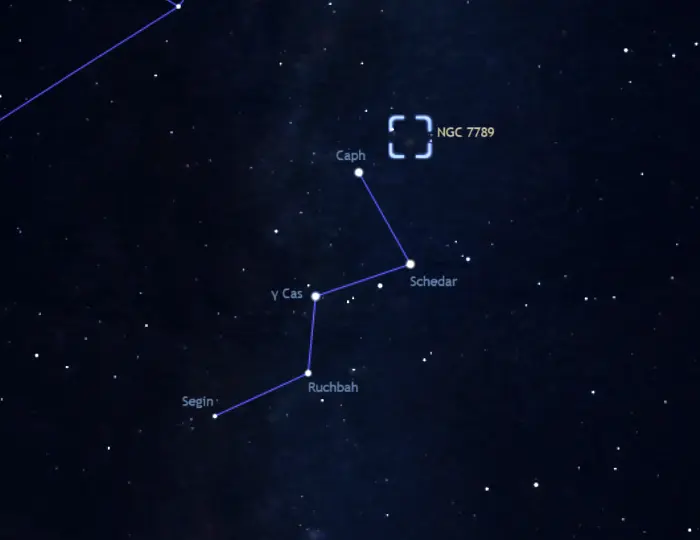
The location of Caroline’s Rose Cluster (NGC 7789) in Cassiopeia, image: Stellarium
At declination 56°42’, the cluster is visible from locations north of the latitude 32° S.
The best time of the year to observe Caroline’s Rose and other deep sky objects in Cassiopeia is during the month of November, when the constellation is high above the horizon in the early evening. For observers in the northern hemisphere, the constellation Cassiopeia is circumpolar and can be observed throughout the year.
Caroline’s Rose Cluster – NGC 7789
| Constellation | Cassiopeia |
| Object type | Open cluster |
| Right ascension | 23h 57m 20.2s |
| Declination | +56° 43′ 34″ |
| Apparent magnitude | 6.7 |
| Apparent size | 25.3 arcminutes |
| Distance | 7,622 light-years (2,337 parsecs) |
| Mass | 6,620.4 ± 762.5 M☉ |
| Age | 1.7 billion years |
| Names and designations | Caroline’s Rose Cluster, Caroline’s Rose, White Rose Cluster, NGC 7789, Collinder 460 (Cr 460), Melotte 245 (Mel 245) |