The Starfish Nebula (IRAS 19024+0044) is a large multipolar protoplanetary nebula located approximately 11,000 light years away in the constellation Aquila (the Eagle). With an apparent size of 3.7 by 2.3 arcseconds, it cannot be observed in small and medium telescopes.
The Starfish Nebula has an unusual appearance with at least six elongated lobes. The lobes emanate from the nebula’s centre, where an evolved star is shedding its outer layers. The central portion of the nebula contains two dark bands that extend northeast and southwest of what is believed to be either a pair of dusty toroidal structures or a single wide toroid.
As the central star approaches the final stage of its evolutionary cycle, it is expelling material at an accelerated rate. The ejected material forms clouds of dust and gas that resemble a starfish.
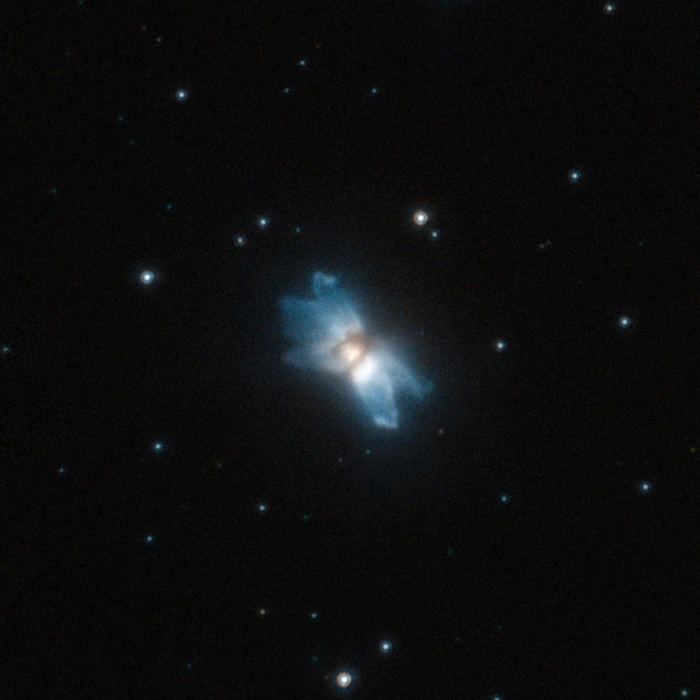

In the constellation of Aquila (the Eagle), lies a star nearing the end of its life that is surrounded by a starfish-shaped cloud of gas and dust. A striking image of this object, known as IRAS 19024+0044 has been captured by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Protoplanetary nebulae offer glimpses of how stars similar to the Sun end their lives and how they make the transition to white dwarfs surrounded by planetary nebulae. As it ages, a Sun-like star eventually sheds its outer layers into space, creating a beautiful and often intricately shaped cloud of gas and dust around it. At first, still relatively cool, the star is unable to ionise this gas, which shines only by reflected and scattered stellar light. Only when the temperature of the star increases enough to ionise this protoplanetary nebula does the pattern of gas and dust become a fully fledged planetary nebula. Protoplanetary nebulae are relatively rare and short-lived objects that provide astronomers with clues into how the often strangely asymmetric planetary nebulae are formed. Clearly visible in this image are five blue lobes that extend away from the central star and give the nebula its asymmetric starfish shape. While astronomers have come up with theories for the origin of these structures, such as direction-changing jets or ejections of matter from the star, their formation is not entirely understood. IRAS 19024+0044 is blue in colour as the blue component of the light coming from the star is more easily scattered by the gas and dust in the nebula, while the red and orange rays are relatively unaffected. This is similar to what happens to sunlight in the Earth’s atmosphere, giving the sky its distinctive shade of blue. This picture was created from images taken with the High Resolution Channel of Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. It is a composite image created by the combination of exposures taken through a yellow–orange filter (F606W, coloured blue) and a near-infrared filter (F814W, coloured red). Image credit: ESA/Hubble, NASA and R. Sahai (CC BY 3.0)
Protoplanetary nebulae are short-lived objects that last less than 10,000 years. They are the transitional phase between the asymptotic giant branch (AGB) and planetary nebula phases. During the pre-planetary nebula stage, the central star is still not hot enough to ionize the surrounding nebula, and the nebula only reflects the star’s light.
As the central stellar remnant becomes hotter and reaches a temperature of about 30,000 K, it begins to produce enough ultraviolet radiation to ionize the expelled material. At this point, the nebula becomes a planetary nebula. Unlike pre-planetary nebulae, which are reflection nebulae, planetary nebulae are emission nebulae. They emit their own light.
The Starfish Nebula has an asymmetric shape with multiple lobes and a very faint, diffuse halo that surrounds the lobes. The halo is composed of material ejected by the star in the past several thousand years, during the AGB phase. Two of the nebula’s lobes have limb-brightened tips with point-symmetric structure relative to the location of the central star.
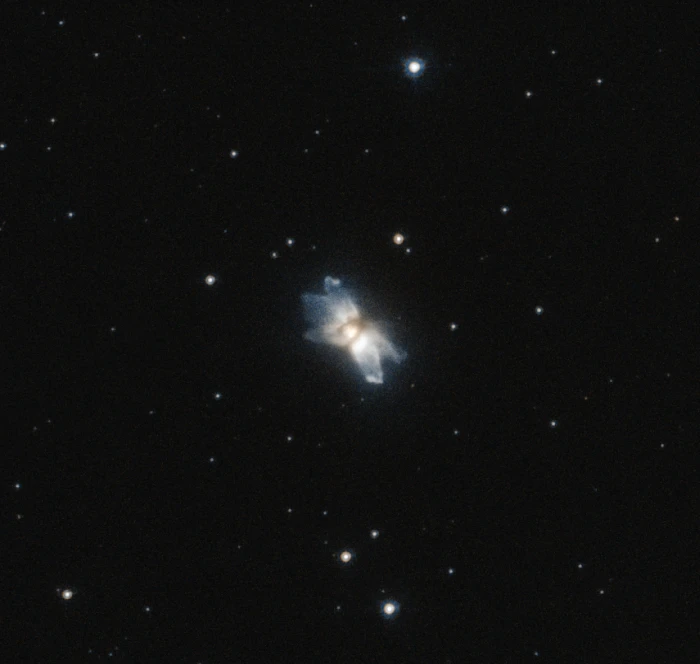

The Starfish Nebula, image credit: Judy Schmidt (CC BY 2.0)
Facts
The Starfish Nebula was confirmed to be a pre-planetary nebula based on observations with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in 2004. A team led by Raghvendra Sahai of the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) imaged the OH/IR star IRAS 19024+0044 at optical and near-infrared wavelengths as part of a survey of protoplanetary nebulae. The astronomers found that the spectral type of the central star is most likely early G (G5 – G0).
The team reported a molecular envelope about 5.5 by 4.4 arcseconds across with an expansion velocity of 13 km s-1. The envelope was resolved interferometrically using the Owens Valley Radio Interferometer. It was produced by the slow, dense wind from the central AGB star. The team found a luminosity of 2,850 solar luminosities, a kinematic distance of 3.5 kiloparsecs (11,415 light-years) based on the star’s radial velocity, and an expansion age of up to 2,870 years. The estimated initial mass of the central star is 1 – 1.5 solar masses, while the lobes have an estimated mass of about 0.02 solar masses.
Location
The Starfish Nebula lies in the equatorial constellation of Aquila. It appears only 48 arcminutes north of the celestial equator, in the rich field of the Milky Way’s bright band. It lies about a third of the way from Lambda Aquilae to Okab (Zeta Aquilae).
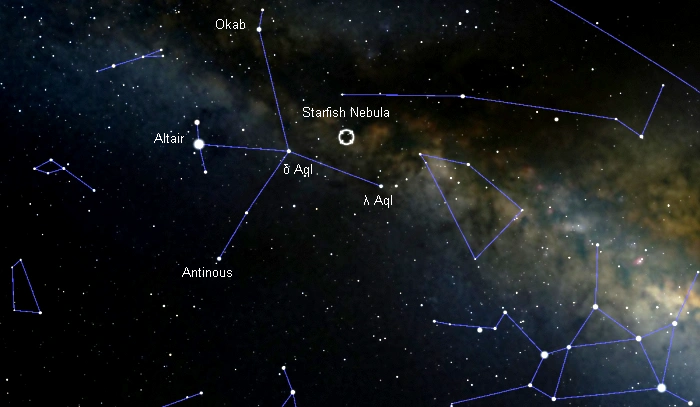
The location of the Starfish Nebula, image: Stellarium
Starfish Nebula – IRAS 19024+0044
| Constellation | Aquila |
| Object type | Protoplanetary nebula |
| Right ascension | 19h 05m 02.0381133528 s |
| Declination | +00° 48′ 50.467761000 ″ |
| Apparent size | 3′′.7 x 2′′.3 |
| Distance | 11,000 light-years (3,373 parsecs) |
| Names and designations | Starfish Nebula, PN G035.2-02.6, IRAS 19024+0044, 2MASS J19050205+0048508, MSX6C G035.2084-02.6528, OH 035.21-02.65, OH 035.209-02.653, OH 035.2-02.6, AKARI-IRC-V1 J1905021+004850, DENIS J190502.0+004850, GLMP 870, TIC 178313423, WISEA J190502.05+004851.0, WISE J190502.06+004850.9, Gaia DR3 4267446485598022272 |