The Hockey Stick Galaxy is a warped barred spiral galaxy located approximately 30 million light years away in the constellation Canes Venatici (the Hunting Dogs). Also known as the Crowbar Galaxy, it has an apparent visual magnitude of 11.0 and an apparent size of 12.9 arcminutes. It has the designations NGC 4656 and NGC 4657 in the New General Catalogue.
The Hockey Stick Galaxy has a diameter of 78,500 light-years and appears edge-on when seen from Earth. It lies in the same area as the Whale Galaxy (NGC 4631). It is receding from us at 650 km/s.
The celestial hockey stick is highly warped because it is interacting with the brighter Whale Galaxy and its companion, the dwarf elliptical galaxy NGC 4627. The Hockey Stick Galaxy is itself a gravitationally bound companion of the larger Whale Galaxy. The two galaxies are less than 500,000 light years apart.
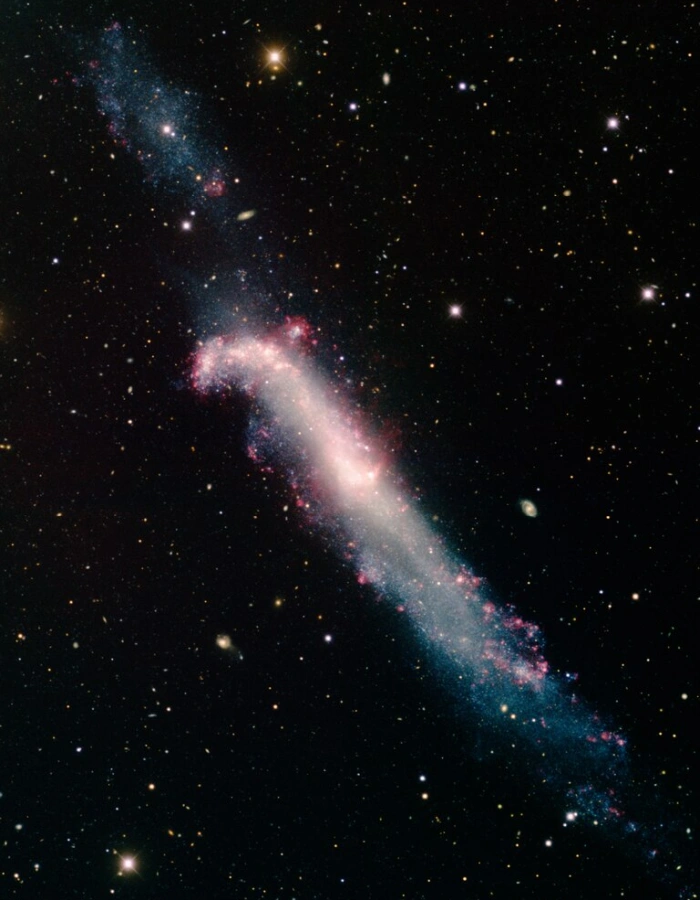

This image was obtained with the wide-field view of the Mosaic camera on the Mayall 4-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory. NGC 4656, also known informally as the “hockey stick galaxy,” is a distorted edge-on spiral galaxy. Its distinctive shape is due to a recent gravitational interaction with the galaxy NGC 4631. It is not yet certain, but these two galaxies may be in the early stages of merging. The faint object in the upper-left corner may not be part of the galaxy, but instead be a dwarf galaxy in the process of merging with NGC 4656. The image was generated with observations in the B (blue), V (green), I (orange) and Hydrogen-Alpha (red) filters. In this image, North is up, East is to the left. Image credit: T.A. Rector (University of Alaska Anchorage) and H. Schweiker (WIYN and NOIRLab/NSF/AURA) (CC BY 4.0)
The gravitational interaction has distorted both galaxies and triggered bursts of star formation, giving NGC 4656 its distinctive shape and appearance.
NGC 4656 is a member of the NGC 4631 Group, a group of galaxies located about 25 million light years away in the constellations Canes Venatici and the neighbouring Coma Berenices. The galaxy group lies within the larger Virgo Supercluster. It is named after its brightest member, the Whale Galaxy (NGC 4631) and also includes the Whale’s close companion, the dwarf galaxy NGC 4627.
The Whale Galaxy is a bright barred spiral galaxy with an elongated, distorted shape and a bright starburst region in the “head” of the whale that gives it its popular nickname. The Whale Galaxy and the Hockey Stick Galaxy are a popular target for astrophotographers because they appear in the same wide field of view.
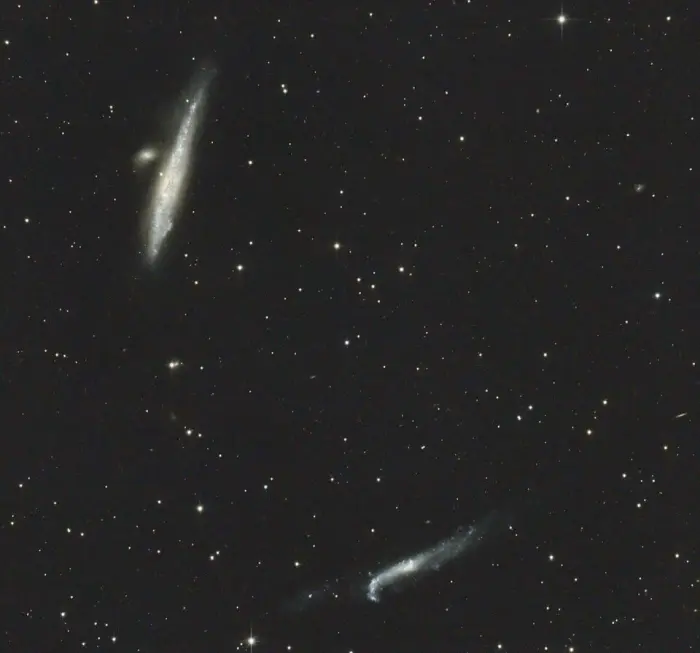

The Whale Galaxy and the Hockey Stick Galaxy, image credit: Sebastian Goralik (CC0 1.0)
Facts
NGC 4656 and NGC 4657 were discovered by the German-born British astronomer William Herschel on March 20, 1787.
The Hockey Stick Galaxy has two separate designations in the New General Catalogue because both William Herschel and Danish astronomer John Louis Emil Dreyer saw the patch of intense star formation (NGC 4657) in the bright northeastern edge of the galaxy as a separate “nebula” from the rest of the galaxy. The patch forms the “blade” of the hockey stick. The Simbad database also lists NGC 4656 and NGC 4657 as two objects, NGC 4656 as a barred spiral galaxy and NGC 4657 as an irregular galaxy.
The Hockey Stick Galaxy hosted a super-outburst of a luminous blue variable (LBV), observed on March 21, 2005. The optical transient source was catalogued as N4656-OT and had an apparent magnitude of 18.0 at the peak. In 2008, the post-outburst source was fainter than magnitude 26.
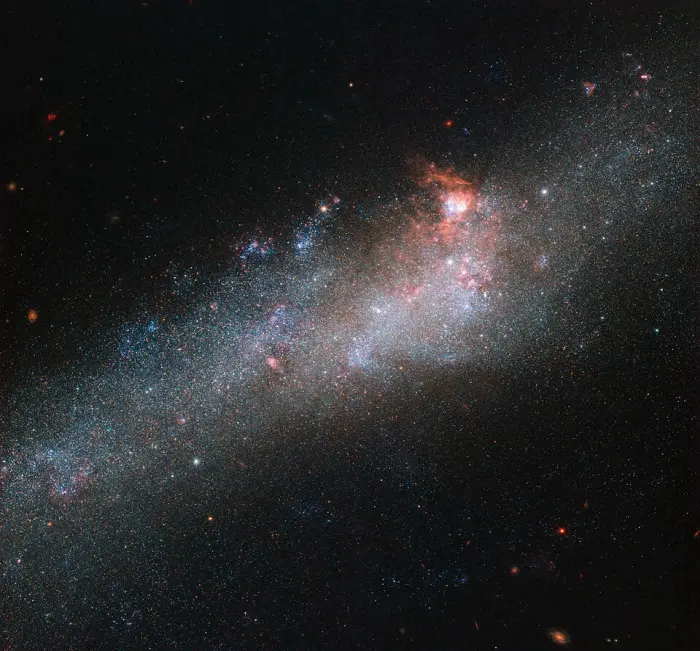

The star of this Hubble Picture of the Week is a galaxy known as NGC 4656, located in the constellation of Canes Venatici (The Hunting Dogs). However, it also has a somewhat more interesting and intriguing name: the Hockey Stick Galaxy! The reason for this is a little unclear from this partial view, which shows the bright central region, but the galaxy is actually shaped like an elongated, warped stick, stretching out through space until it curls around at one end to form a striking imitation of a celestial hockey stick. This unusual shape is thought to be due to an interaction between NGC 4656 and a couple of near neighbours, NGC 4631 (otherwise known as The Whale Galaxy) and NGC 4627 (a small elliptical). Galactic interactions can completely reshape a celestial object, shifting and warping its constituent gas, stars, and dust into bizarre and beautiful configurations. The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has spied a large number of interacting galaxies over the years, from the cosmic rose of Arp 273 to the egg-penguin duo of Arp 142 and the pinwheel swirls of Arp 240. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA (CC BY 4.0)
Location
The Hockey Stick Galaxy lies in the faint constellation of Canes Venatici, roughly halfway between Alkaid in the Big Dipper’s handle and Denebola at the Lion’s tail. It appears in the region between Cor Caroli, the brightest star in Canes Venatici, and the fainter Gamma Comae Berenices in Coma Berenices, just north of the bright, large Coma Star Cluster. The Whale Galaxy appears 6 degrees south of Cor Caroli, in direction of the brighter Denebola. NGC 4656 and NGC 4657 appear almost half a degree southeast of the cosmic Whale.
At declination 32° 10’, the Hockey Stick Galaxy is visible from locations north of the latitude 57° S. It is best seen from the northern hemisphere.
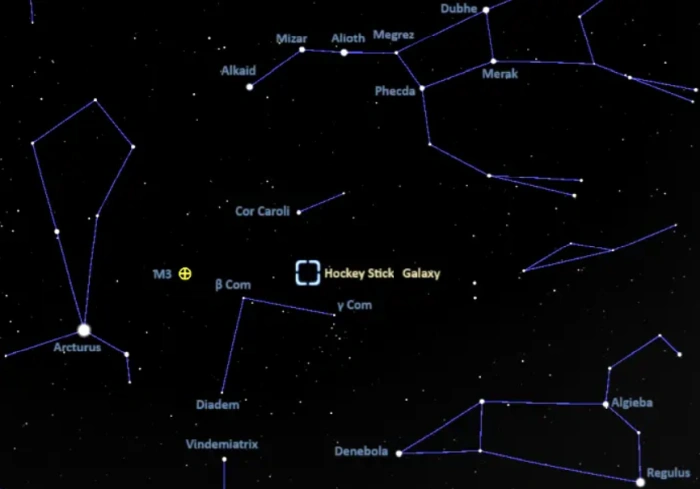
The location of the Hockey Stick Galaxy, image: Stellarium
The best time of the year to observe the Hockey Stick Galaxy, the Whale Galaxy, and other deep sky objects in Canes Venatici is during the month of May, when the constellation appears higher above the horizon in the early evening.
Hockey Stick Galaxy – NGC 4656 and NGC 4657
| Constellation | Canes Venatici (the Hunting Dogs) |
| Object type | Barred spiral galaxy |
| Morphological type | SB(s)m pec or SB |
| Right ascension | 12h 43m 57.6889089768s |
| Declination | +32° 10′ 13.345914504 ″ |
| Apparent magnitude | 11.0 |
| Apparent size | 12.9’ |
| Distance | 30 million light-years (9.2 megaparsecs) |
| Redshift | 0.002171 |
| Heliocentric radial velocity | 650 km/s |
| Names and designations | Hockey Stick Galaxy, Hockey Stick Galaxies, Crowbar Galaxy, NGC 4656 and NGC 4657 |
| NGC 4656 | LEDA 42863, PGC 42863, UGC 7907, MCG+05-30-066, BTS 153, PSCz Q12415+3226, CAIRNS J124358.29+321014.2, FGCA 174A, IRAS 12415+3226, IRAS F12415+3227, KPG 350b, KUG 1241+324, LCSB L533, LJHY 109, RX J1243.9+3210, 2MASX J12435764+3210130, 2MASXI J1243582+321010, TC 239, Z 159-65, Z 1241.6+3227, SDSS J124405.97+321232.3, SDSS J124357.69+321013.3, UZC J124358.3+321014 |
| NGC 4657 | IRAS 12417+3228, IRAS F12416+3228, RX J1244.1+3212, SDSS J124411.17+321221.6, SDSS J124411.16+321221.6, PSCz Q12417+3228, 1RXS J124410.2+321252 |
Images
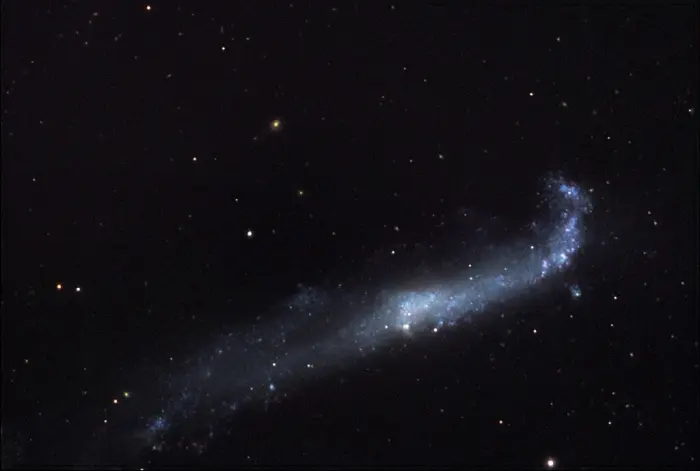

NGC 4656 is the “disturbed” neighbor to NGC 4631. The gravitational tug-of-war warps the disk of this galaxy. The nearness of the galaxy (perhaps 25 million light years away) allows small knotted star forming regions to be resolved. There are also quite a few background galaxies in the picture. This image was taken as part of Advanced Observing Program (AOP) program at Kitt Peak Visitor Center during 2014. Image credit: KPNO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/Doug Matthews/Adam Block (CC BY 4.0)
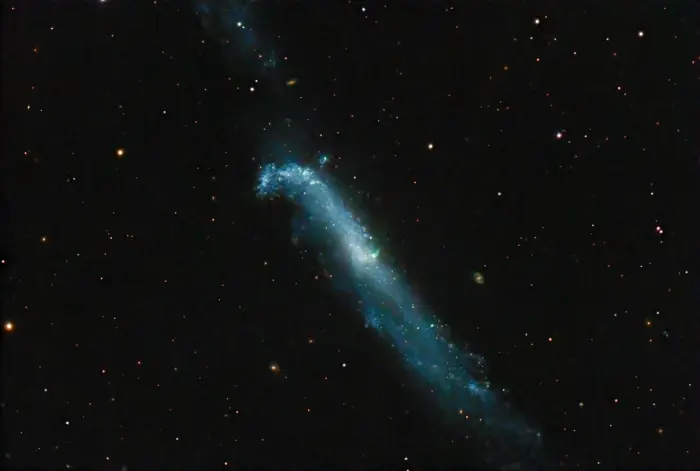

The Hockey Stick Galaxy, image credit: Wikimedia Commons/Juan Lacruz (CC BY 4.0)
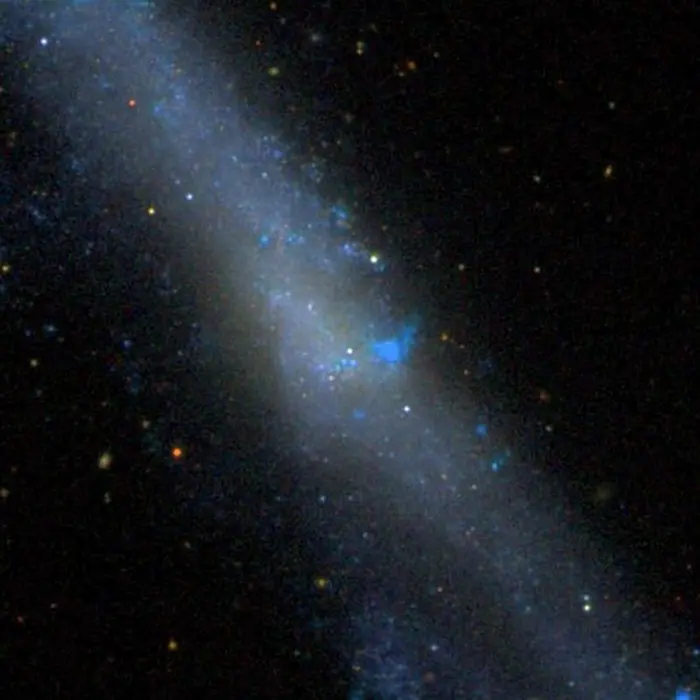

NGC 4656, image: Sloan Digital Sky Survey (CC BY 4.0)