HCG 87 (Hickson Compact Group 87) is a group of galaxies located approximately 400 million light-years away in the constellation Capricornus. Three of the galaxies are physically interacting and form a tight group. The small spiral galaxy that appears in the centre of the group is believed to lie at a much greater distance.
The compact group of galaxies has a diameter of around 170,000 light-years, corresponding to an angular size of 1.5 arcminutes. It consists of the edge-on spiral galaxy HCG 87a, the bright elliptical galaxy HCG 87b, and the spiral galaxy HCG 87c.
The smaller spiral HCG 87d in the middle is believed to be a background galaxy. Several other smaller and fainter galaxies appear in the same field of view. These also lie beyond the brighter members of the compact group.
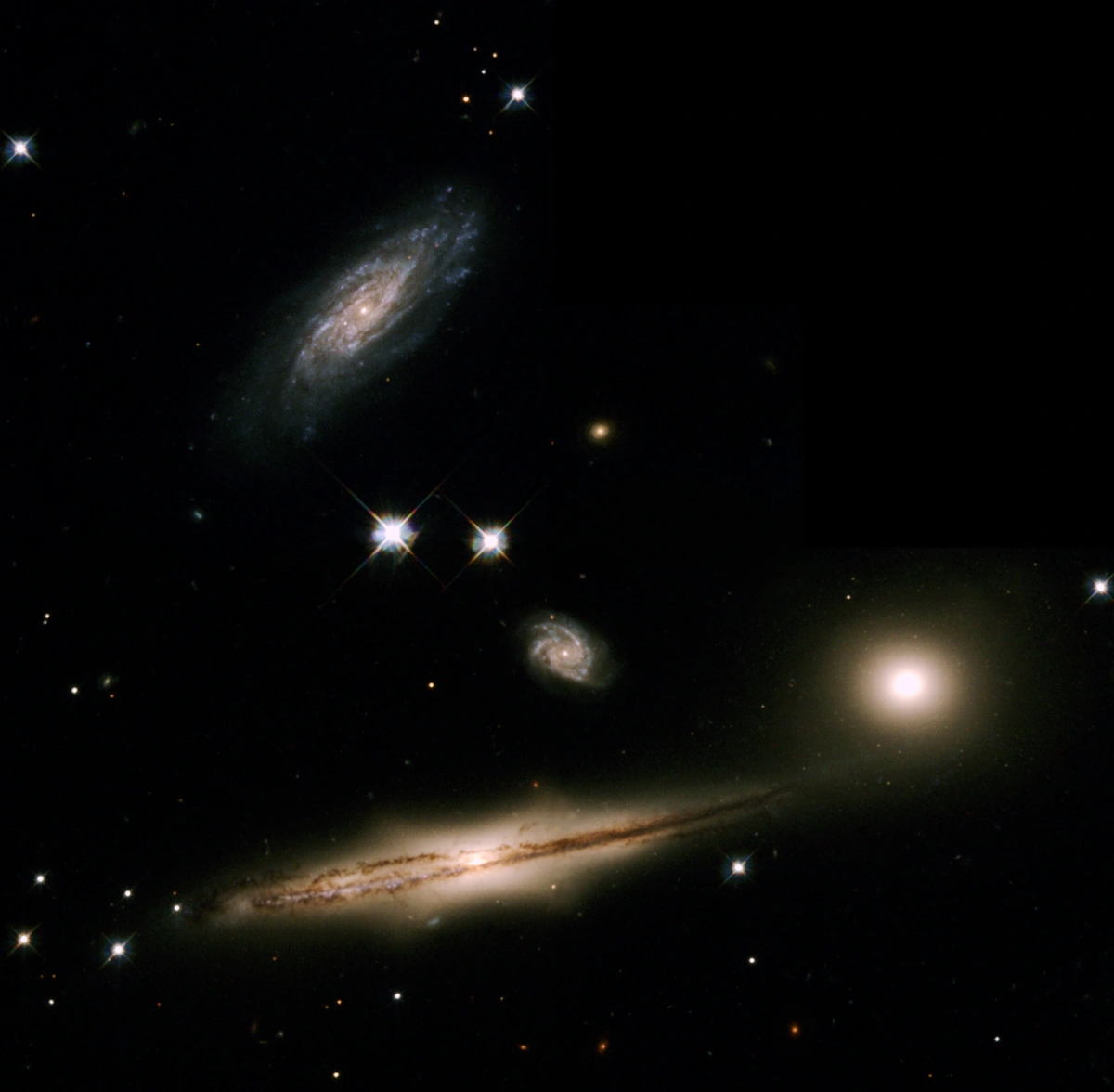

This troupe of four galaxies, known as Hickson Compact Group 87 (HCG 87), is performing an intricate dance orchestrated by the mutual gravitational forces acting between them. The dance is a slow, graceful minuet, occurring over a time span of hundreds of millions of years. Image credit: The Hubble Heritage Team (AURA/STScI/NASA/ESA) (CC BY 4.0)
The triplet of galaxies that form HCG 87 are quite faint. The large spiral galaxy HCG 87a has an apparent visual magnitude of 15.3 and an apparent size of 1.130 by 0.271 in the near-infrared band. The disk-shaped galaxy appears nearly edge-on and has a prominent dust lane. It lies approximately 383.37 million light-years away.
HCG 87b is an elliptical or lenticular galaxy that appears very close to HCG 87a. It has an apparent magnitude of 15.4 and an apparent size of 0.490 by 0.343 arcminutes. The galaxy lies around 396.77 million light years away. Imaging with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) has revealed a faint tidal bridge of stars between HCG 87b and the edge-on spiral HCG 87a.
HCG 87c is a spiral galaxy with an apparent magnitude of 16.1 and an angular size of 0.430 by 0.198 arcminutes. It lies approximately 341.52 million light-years away.
The galaxies’ proximity to each other and mutual interaction has left all three members of HCG 87 disrupted. Their gravitational forces have greatly affected each other’s structure and evolution. The galaxies HCG 87a and HCG 87b host active galactic nuclei (AGNs) with black holes that are accreting gas. HCG 87c may be experiencing a starburst.
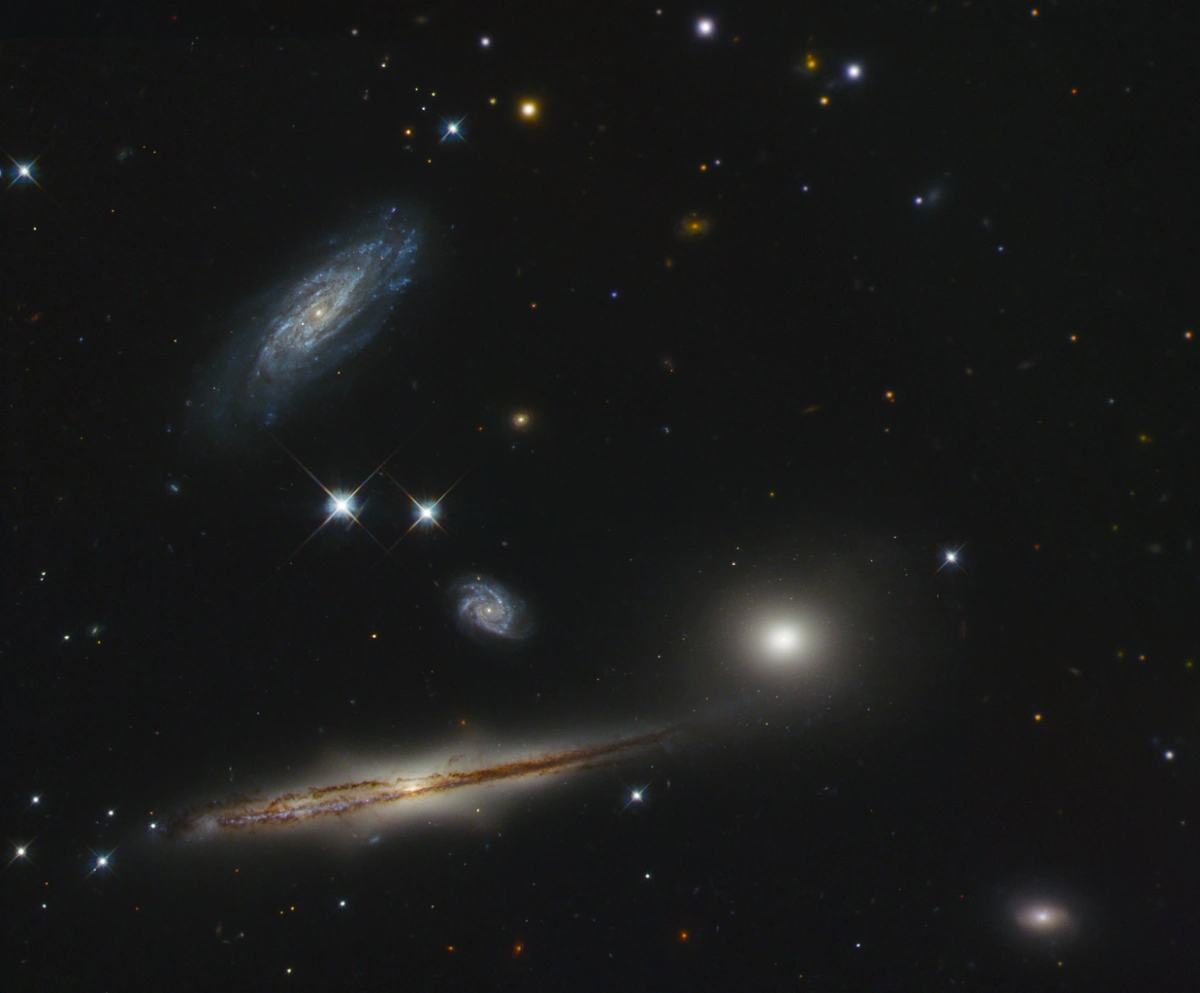

Hickson Compact Group 87 (HCG 87) in near-infrared and visible light. Image credit: Judy Schmidt (CC BY 2.0)
HCG 87d, the smaller galaxy that appears in the same field of view, is a spiral galaxy with an apparent magnitude of 17.8. It has a larger redshift than the three brighter galaxies and is probably not gravitationally bound to the group.
In 1997, astronomers identified a total of six members of the compact group based on an analysis of the structural and dynamical properties of the group. The galaxies HCG 87a, HCG 87b and HCG 87c form the core of the group with two other galaxies, and the sixth galaxy lies in the group’s halo. The astronomers categorized the group as a compact quintet with a sixth neighbour that is either orbiting the group or falling into it.
The compact group of galaxies was included in the Hickson Compact Group catalogue by Paul Hickson, Department of Geophysics and Astronomy, University of British Columbia, in 1982. These galaxies were identified on prints obtained using the 48-inch Oschin Schmidt telescope at Mount Palomar during the Palomar Observatory Sky Survey in the 1950s.
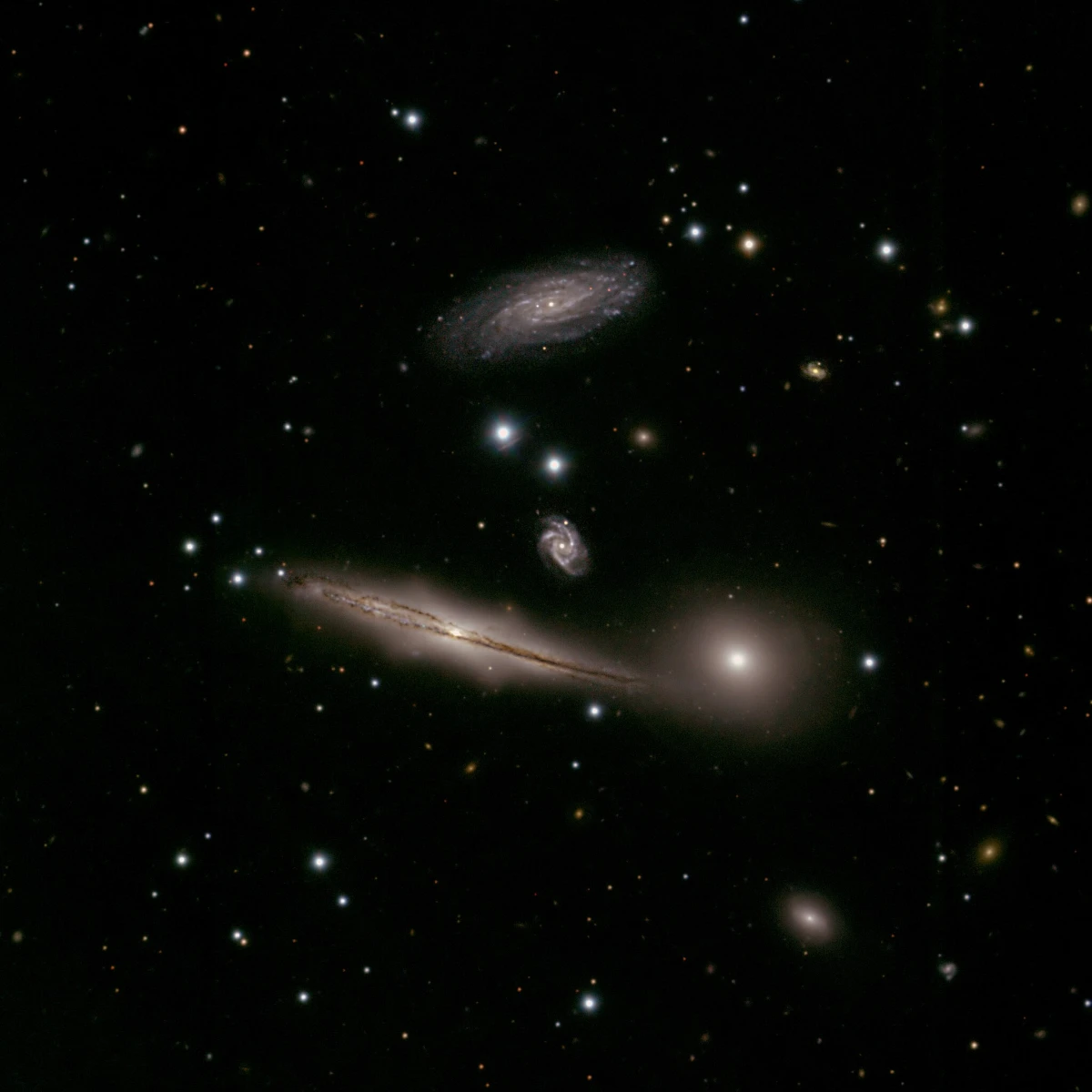

During commissioning in early 2003 of the Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph (GMOS) on the Gemini South Telescope, images and spectra were obtained of the group of galaxies known as the Hickson Compact Group 87 (HCG 87). The Gemini image compares very favorably with space-based image of this same field and illustrates the remarkable resolution that is possible with Gemini when atmospheric conditions are optimal. Image credit: International Gemini Observatory (CC BY 4.0)
Location
The Hickson Compact Group 87 lies in the faint zodiac constellation of Capricornus (the Sea Goat). It appears about a third of the way from Pi Capricorni to Zeta Capricorni.
The faint, V-shaped constellation figure of Capricornus can be found using the brighter stars of Aquila (the Eagle). A line extended through the Shaft of Aquila, formed by the bright Altair with the fainter Tarazed and Alshain, points in the general direction of the right side of the V pattern.
The best time of the year to observe deep sky objects in Capricornus is during the month of September, when the constellation appears high above the horizon in the early evening. The galaxies of HCG 87 are too faint and small to be observed in small and medium telescopes.
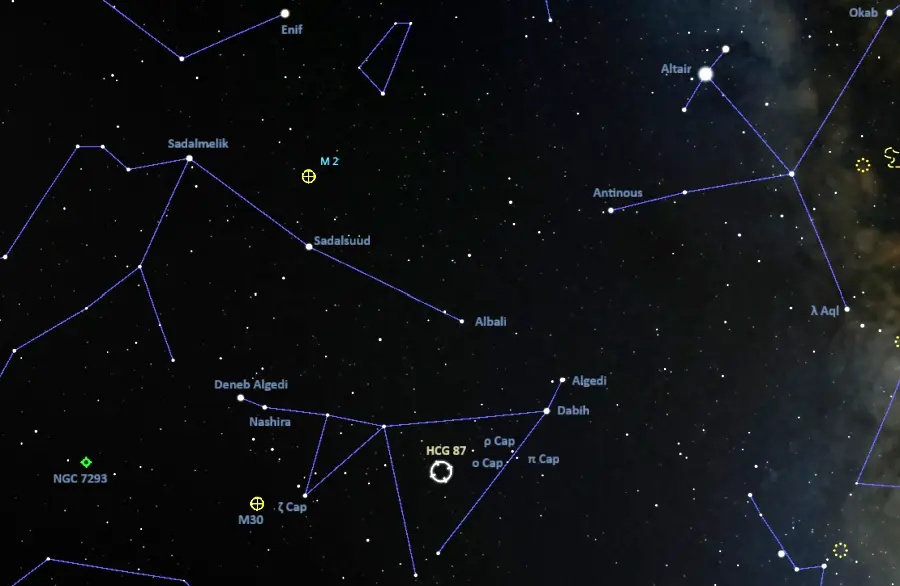
HCG 87 location, image: Stellarium
HCG 87
| Constellation | Capricornus |
| Object type | Compact galaxy group |
| Right ascension | 20h 48m 11.9s |
| Declination | −19° 50′ 35″ |
| Apparent size | 1.5′ x 1.5′ |
| Distance | 400 million light-years (120 megaparsecs) |
| Diameter | 170,000 light-years (52 kiloparsecs) |
| Names and designations | Hickson Compact Group 87, HCG 87 |
HCG 87a
| Object type | Spiral galaxy |
| Morphological type | Sb |
| Right ascension | 20h 48m 14.7948630048s |
| Declination | −19° 50′ 57.268042908″ |
| Apparent magnitude | 15.3 |
| Apparent size | 1.130′ x 0.271′ |
| Distance | 383.37 million light-years (117.54 megaparsecs) |
| Redshift | 0.029433 ± 0.000117 |
| Heliocentric radial velocity | 8,443 ± 14 km/s or 8,694 km/s |
| Names and designations | HCG 87a, ESO 597-36, LEDA 65415, PGC 65415, MCG-03-53-005, 2MASX J20481480-1950571, 2MFGC 15760, SGC 204523-2002.0, dCAZ94 HCG 87-01, dCAZ94 HCG 87-01a, 6dFGS gJ204814.8-195057, Gaia DR3 6857276786872588160, [CHM2007] HDC 1127 J204814.80-1950571, [CHM2007] LDC 1424 J204814.80-1950571, [KK2000] 63C |
HCG 87b
| Object type | Lenticular or elliptical galaxy |
| Morphological type | E-S0 |
| Right ascension | 20h 48m 10.7356125720s |
| Declination | −19° 51′ 21.790867536″ |
| Apparent magnitude | 15.4 |
| Apparent size | 0.490′ x 0.343′ |
| Distance | 396.77 million light years (121.65 Mpc) |
| Redshift | 0.030389 ± 0.000217 |
| Heliocentric radial velocity | 8,740 ± 20 km/s or 8,972 ± 65 km/s |
| Names and designations | HCG 87b, LEDA 65409, PGC 65409, MCG-03-53-003, 2MASX J20481076-1951221, SGC 204519-2002.5, NPM1G -20.0515, Gaia DR3 6857276821232326400, [CHM2007] LDC 1424 J204810.76-1951221, [CHM2007] HDC 1127 J204810.76-1951221, dCAZ94 HCG 87-03, dCAZ94 HCG 87-03b, 6dFGS gJ204810.8-195122, [KK2000] 63A |
HCG 87c
| Object type | Spiral galaxy |
| Morphological type | Sb or Sc |
| Right ascension | 20h 48m 11.8006072944s |
| Declination | −19° 49′ 54.648151824″ |
| Apparent magnitude | 16.1 |
| Apparent size | 0.430′ x 0.198′ |
| Distance | 341.52 Mly (104.71 Mpc) |
| Redshift | 0.030210 ± 0.000444 |
| Heliocentric radial velocity | 8,914 ± 7 km/s or 8,920 ± 133 km/s |
| Names and designations | HCG 87c, ESO 597-35, LEDA 65412, PGC 65412, MCG-03-53-004, dCAZ94 HCG 87-04, dCAZ94 HCG 87-04c, 6dFGS gJ204811.8-194955, Gaia DR3 6857277615802144256 |
HCG 87d
| Object type | Spiral galaxy |
| Morphological type | Sd or Sc |
| Right ascension | 20h 48m 12.7970828160s |
| Declination | −19° 50′ 46.023701244″ |
| Apparent magnitude | 17.8 |
| Apparent size | 0.217′ x 0.143′ |
| Redshift | 0.034623 ± 0.000534 |
| Heliocentric radial velocity | 10,200 ± 160 km/s |
| Names and designations | HCG 87d, LEDA 65414, PGC 65414, 2MASX J20481275-1950461, Gaia DR3 6857276821231615232 |