Alcyoneus is a large radio galaxy located approximately 3.5 billion light-years away in the northern constellation of Lynx. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 17.16 and an apparent size of 14.07 arcseconds. The galaxy cannot be observed in amateur telescopes.
Alcyoneus’s lobed structures span 5 megaparsecs (16 million light years), forming the second largest radio structure discovered in any galaxy. At the time of discovery, the huge jets were the largest ever detected. For this reason, some media outlets called Alcyoneus the largest galaxy known when the discovery was announced in 2022. A galaxy with even larger radio ejecta was discovered two years after Alcyoneus. The cause of the giant radio galaxy growth is still not well understood.
Alcyoneus is classified as a Fanaroff-Riley class II radio galaxy, indicating a luminous galaxy with bright edges and bright patches at the ends of its lobes. The radio source resides in the host galaxy catalogued as SDSS J081421.68+522410.0 in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey’s data release.
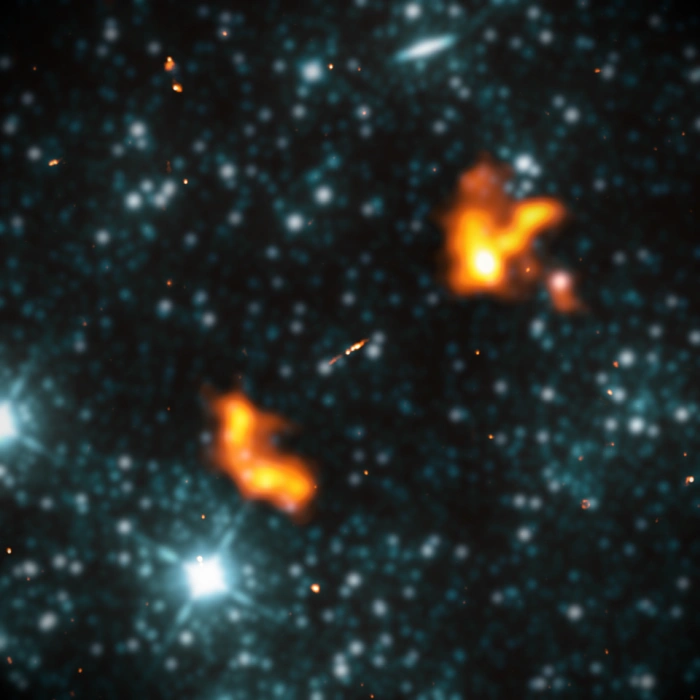

False-colour image showing a 2048 arcsecond by 2048 arcsecond solid angle centred around Alcyoneus’ host galaxy, J081421.68+522410.0, with LOFAR radio data at 144 MHz (orange) and WISE infrared data at 3.4 micron (blue) overlaid. To draw attention to the radio emission, the infrared emission has been blurred. Image credit: Martijn Oei (CC BY-SA 4.0)
The radio galaxy’s giant radio lobes are produced by relativistic jets powered by the galaxy’s central supermassive black hole. The host galaxy is a relatively quiescent, normal elliptical galaxy embedded in a filament of the cosmic web. It has a star formation rate of only 0.016 solar masses per year and is classified as a low excitation radio source. The galaxy does not contain a quasar. Most of its energy does not come from its active galactic nucleus, but from the central jet.
Despite the enormous size of the galaxy’s radio emissions, the galaxy itself has an ordinary luminosity in radio wavelengths, as well as ordinary stellar mass and mass of the central supermassive black hole.
The black hole ejects some of its accretion disk plasma along the two magnetised jets that are aligned with the rotation axis. The relativistic electrons in the massive plasma plumes generate synchrotron radiation that can be detected with radio telescopes. The jet streams themselves ultimately enrich the intergalactic medium with cosmic rays and magnetic fields.
The host galaxy contains a supermassive black hole with a mass of around 390 million solar masses, which is a normal mass for an elliptical galaxy. The galaxy has a stellar mass of 240 billion solar masses.
It is still unclear how the extent of Alcyoneus’s radio emissions got to be so large. Astronomers have proposed that the cosmic web environment around Alcyoneus may be less dense that around similar galaxies, which may facilitate growth.
Alcyoneus has an isophotal diameter of 242,700 light-years. While it is much larger than the Milky Way (87,400 ly), the galaxy is dwarfed by the likes of ESO 383-76, IC 1101, and the Condor Galaxy (NGC 6872).
ESO 383-76, a colossal X-ray luminous supergiant elliptical galaxy, is the brightest cluster galaxy of the Abell 3571 galaxy cluster in the constellation Centaurus. It has a major axis diameter of 1,764,000 light-years, a minor axis diameter of 882,100 light-years, and an isophotal diameter of 453,000 light-years.
Another previous record holder, the supergiant lenticular galaxy IC 1101 in the constellation Virgo, has an isophotal diameter of 403,300 to 553,200 light-years. The Condor Galaxy (NGC 6872) in the constellation Pavo, the largest spiral galaxy known, has an isophotal diameter of 717,000 light-years.
If radio plumes were considered part of the host galaxy, a diameter of 16 million light years would place Alcyoneus near the top of the list of the largest galaxies known. However, since the plumes are ejected material, they are not part of the host galaxy, and their extent is not considered when determining the galaxy’s size.
Facts
The Alcyoneus galaxy was discovered by a team of astronomers led by Martijn Oei of the Leiden Observatory, University of Leiden, the Netherlands, in the data obtained during the Low-Frequency Array (LOFAR) Two-metre Sky Survey (LoTSS) in 2022. The discovery was announced in Astronomy & Astrophysics. The interferometric radio survey of the northern sky revealed more than 8,000 previously undiscovered giant radio galaxies, including Alcyoneus.
The astronomers reported a giant radio galaxy with a projected length of 4.99 ± 0.04 megaparsecs (16,275,203.25 ± 130,462.55 light years). They described the object as the largest known structure of galactic origin and named it Alcyoneus. Subsequent studies confirmed that the two large radio galaxy lobes were produced by the same source.
The galaxy appears in the faint northern constellation of Lynx, in the region between Muscida (Omicron Ursae Majoris) at the Great Bear’s snout and the orange giant Alsciaukat (31 Lyncis) in Lynx.
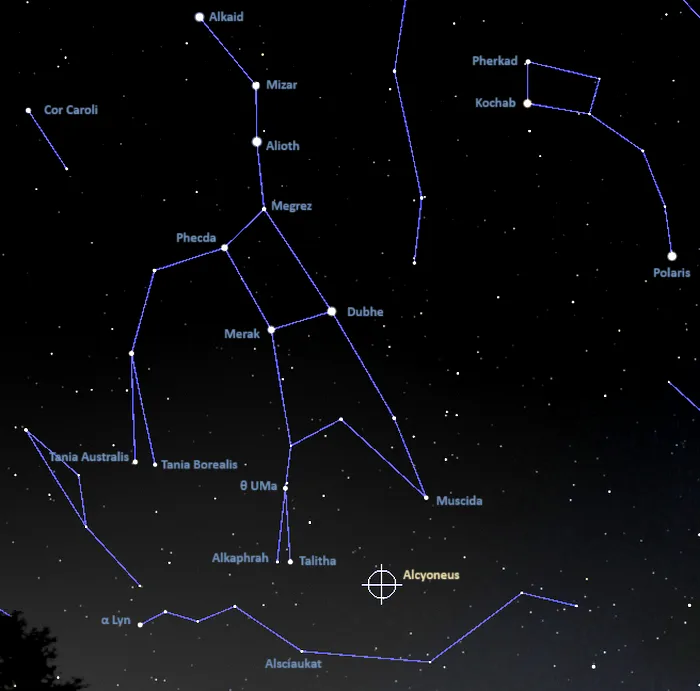
The approximate location of Alcyoneus, imae: Stellarium
As of 2024, Alcyoneus is the second largest object of its kind, after the giant radio galaxy J152932.16+601534.4, named Porphyrion. Located in the constellation Draco, Porphyrion was discovered by the same team that found Alcyoneus. The galaxy’s lobes span 7 megaparsecs (23 million light years) across.
Both Alcyoneus and Porphyrion were named after the largest of the Giants (Gigantes), the offspring of Gaia and Uranus (Ouranos) in Greek mythology. They are the largest members of a group of about a thousand giant radio galaxies discovered to date. Only about a hundred of these are larger than 2 megaparsecs (6,523,128 light-years), and only ten are larger than 3 megaparsecs (9,784,691 light-years).
Alcyoneus – WISEA J081421.70+522410.0
| Constellation | Lynx |
| Object type | Radio galaxy |
| Morphological type | E (89%) |
| Right ascension | 08h 14m 21.68s |
| Declination | +52° 24′ 10.08″ |
| Apparent magnitude | 17.16 |
| Apparent size | 14.07″ |
| Distance | 3.5 billion light-years (1.1 gigaparsecs) |
| Redshift | 0.24674 ± 0.00006 |
| Heliocentric radial velocity | 73,969.90 ± 17.69 km/s |
| Galactocentric velocity | 74,013 ± 18 km/s |
| Size | 242,700 light-years (74.4 kpc) |
| Mass | 2.4 x 1011 M☉ |
| Names and designations | Alcyoneus, 2MASS J08142169+5224103, WISEA J081421.70+522410.0, SDSS J081421.68+522410.0, SDSS J081421.69+522410.0, SDSS J081421.69+522410.1 |